|
Disclaimer: This content is reviewed periodically and is subject to change as new health information becomes available. The
information provided is intended to be informative and educational and is not a replacement for professional medical evaluation,
advice, diagnosis or treatment by a healthcare professional.
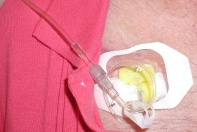
A portacath is a device that is placed under your skin. It is used to inject chemo drugs and obtain blood. With a portacath,
your veins are no longer inserted with needles. This will eliminate an immense amount of strain on your veins.
Testicular cancer chemo treatment requires a lot of chemo drug injections and blood withdrawals that is why a portacath
is highly recommended.
The portacath is the size of a fat quarter.
Portacath placement
the portacath placement is under the skin on your right chest about three inches above your nipple.
It will appear as a bump 1-3 inches high underneath your skin with a catheter going to your collarbone. The catheter flows
from the portacath to a large vein near the collarbone.
Rarely, the portacath placement is on the under arm. This placement is not common because the portacath rubs on your armpit
which could irritate it.
Portacath insertion
When the portacath is used, the skin is carefully cleaned and sterilized to eliminate the chance of infection. A special
needle is used to inject chemo drugs or withdrawal blood.
Your nurse might apply a cream or spray to numb your skin above your portacath. This is applied an hour prior to the needle
insertion.
After every use, the portacath must be flushed with saline and heparin. The saline and heparin keeps blood clots from
forming. The flushing puts a very permanent marker/metallic taste in your mouth.
A portacath must be accessed and flushed every 30 days.
|

